728x90
반응형

1. 셋(Set)
셋(Set): 중복되지 않는 요소들의 집합
2. 공통 메서드
0) 생성
Set<Integer> intHSet = new HashSet<>();
// ⭐️ 간략한 생성 및 초기화 방법들
// 💡 Arrays 클래스 : 배열 관련 각종 기능 제공
Set<Integer> intHSet2A = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
);
// 💡 자바9에서부터 가능
Set<Integer> intHSet2B = new HashSet<>(
List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
);
Set<Integer> intHSet2C = new HashSet<>();
Collections.addAll(ints2C, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
1) 값 추가: add, addAll
// ⭐️add 메서드로 요소 추가
// 중복된 요소는 추가되지 않음!
intHSet.add(11);
intHSet.add(11);
intHSet.add(33);
intHSet.add(44);
intHSet.add(55);
// 현재 컬렉션inst에 컬렉션 C의 모든 데이터를 추가
// 중복된 요소는 추가되지 않음!
intHSet.addAll(C);
2) 값 삭제: remove, removeAll
// ⭐️요소 자체를 지우기 -> return boolean: 있었는지 여부 반환
boolean rm4 = intHSet.remove(4);
boolean rm5 = intHSet.remove(5);
// 컬렉션 intHSet에서 컬렉션 C와 일치하는 데이터를 삭제
intHSet.removeAll(C)
3) 포함여부 확인: contains, containsAll
// 포함 여부 판단
boolean intHSetCon3 = intHSet.contains(33);
boolean intHSetCon6 = intHSet.contains(66);
// 현재 컬렉션ints에 컬렉션 C의 모든 데이터가 포함 여부 판단
boolean intHSetConAll = intHSet.containsAll(C)
4) 요소 개수 확인: size / 빈 셋인지 확인: isEmpty / 모든 데이터 삭제: clear
// 요소 개수
int intsSize = intHSet.size();
// size가 0인지 여부 반환
boolean intsIsEmpty = intHSet.isEmpty();
// 모든 데이터 삭제
intHSet.clear();
5) 교집합: retainAll
Set<Integer> intHSet2A = new HashSet<>(
Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
);
Set<Integer> intHSet2B = new HashSet<>(
List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
);
// 교집합
intHSet2B.retainAll(intHSet2A);
System.out.println(ints2B); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
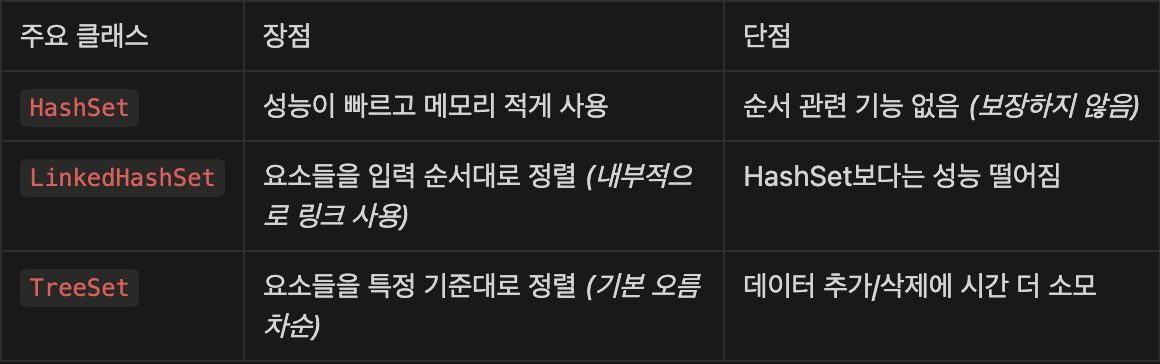
2. HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet
1) LinkedHashSet : 입력된 순서대로 / TreeSet : 오름차순
2) HashSet이 정렬된 것처럼 보이지만 보장된 것이 아님
- Hash 방식에 의한 특정 조건에서의 정렬일 뿐
HashSet<Integer> intHashSet = new HashSet<>();
LinkedHashSet<Integer> intLinkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
TreeSet<Integer> intTreeSet = new TreeSet<>();
for (int i : new int[] { 3, 1, 8, 5, 4, 7, 2, 9, 6}) {
intHashSet.add(i);
intLinkedHashSet.add(i);
intTreeSet.add(i);
}
for (var s : new Set[] {intHashSet, intLinkedHashSet, intTreeSet}) {
System.out.println(s);
}
// HashSet [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
// LinkedHashSet[3, 1, 8, 5, 4, 7, 2, 9, 6]
// TreeSet [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Set<String> strHashSet = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> strLinkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Set<String> strTreeSet = new TreeSet<>();
for (String s : new String[] {
"Fox", "Banana", "Elephant", "Car", "Apple", "Game", "Dice"
}) {
strHashSet.add(s);
strLinkedHashSet.add(s);
strTreeSet.add(s);
}
for (var s : new Set[] {strHashSet, strLinkedHashSet, strTreeSet}) {
System.out.println(s);
}
// HashSet [Apple, Game, Car, Elephant, Dice, Fox, Banana]
// LinkedHashSet[Fox, Banana, Elephant, Car, Apple, Game, Dice]
// TreeSet [Apple, Banana, Car, Dice, Elephant, Fox, Game]- 첫 번째 예시의 경우, HashSet과 TreeSet이 동일해서 HashSet이 정렬된 것 처럼 보인다.
- 두 번째 예시의 경우, TreeSet은 정렬된 반면에 HashSet은 정렬되지 않았다.
- 즉, HashSet은 정렬을 보장하지 않는다.
출처 및 참고) 제대로 파는 자바(Java) - by 얄코(https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%A0%9C%EB%8C%80%EB%A1%9C-%ED%8C%8C%EB%8A%94-%EC%9E%90%EB%B0%94)
728x90
반응형
'우아한테크코스 > 1주차 프리코스' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 1주차 스터디 - 파이썬 list 자바 Array, ArrayList 에 대해! (2) | 2023.10.21 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 컬렉션 - 맵(Map) (0) | 2023.10.21 |
| [1주차 프리코스] 2일차 리뷰 (0) | 2023.10.20 |
| [Java] 컬렉션 - 리스트(List) (1) | 2023.10.20 |
| [1주차 프리코스] 1일차 리뷰 (0) | 2023.10.19 |



